Add sudo users on Ubuntu
In Ubuntu, and the other Linux based systems, the command sudo allows users to run commands with admin ( root ) privileges. This allows a user to perform actions that would otherwise be restricted, such as installing software, modifying system files, and managing other users.
The sudo command allows users to run commands that need root (admin) rights without logging in as root.
By default, Ubuntu, disables root user, so using sudo is the way to go when running commands that needs special privileges.
In order to add a sudo user, you need to do the following steps:
Create a user
First step is to create a new user. For this, you need to login into a root user, or another user with sudo privileges.
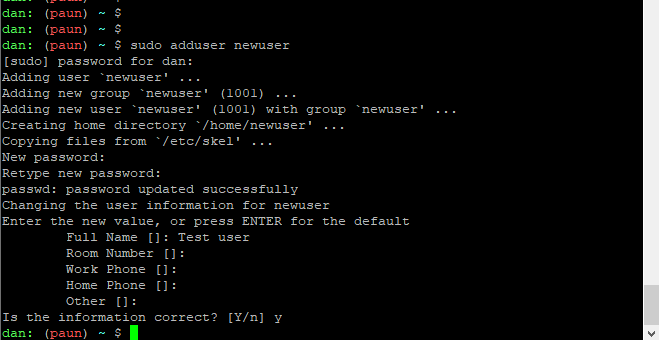
adduser [newuser]Replace newuser with the desired user. The adduser command creates a new user, a new group and a home folder in /home for that user.
The adduser command needs elevated privileges, so if you are not a root user, you need to have sudo privileges to run this command:
sudo adduser [newuser]The system will add the new user, and promt you to enter a password and additional information about the user.
Add the user to sudo group
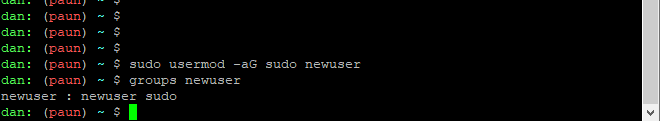
Ubuntu have a group for sudo users. To grant elevated privileges, you need to add the user to the sudo group. This can be done with the following command:
usermod -aG sudo newuserThe usermod command needs also elevated privileges. So, if you get permission error, you have to use the sudo command.
sudo usermod -aG sudo newuser-a is the shortcode for append
G is the shortcut for group
so, the –aG argument tells the system to append the newuser to the sudo group.
In order to verify that the user belongs to sudo group, you can use groups newuser command